Analytical methods that are not standardized in the US Pharmacopeia are non-compendial methods. These methods are product specific and need to be developed based on the critical quality attributes of the product. Following tests constitute non-compendial methods.
What are Identity Tests?
Identity tests are analytical methods used to determine and/or to confirm product identity. These identity tests should be product specific and are based on unique aspects of molecular structure and/or other specific properties of the product. The identity tests can be qualitative as well as quantitative in nature. The following experiments are performed as part of identity testing.
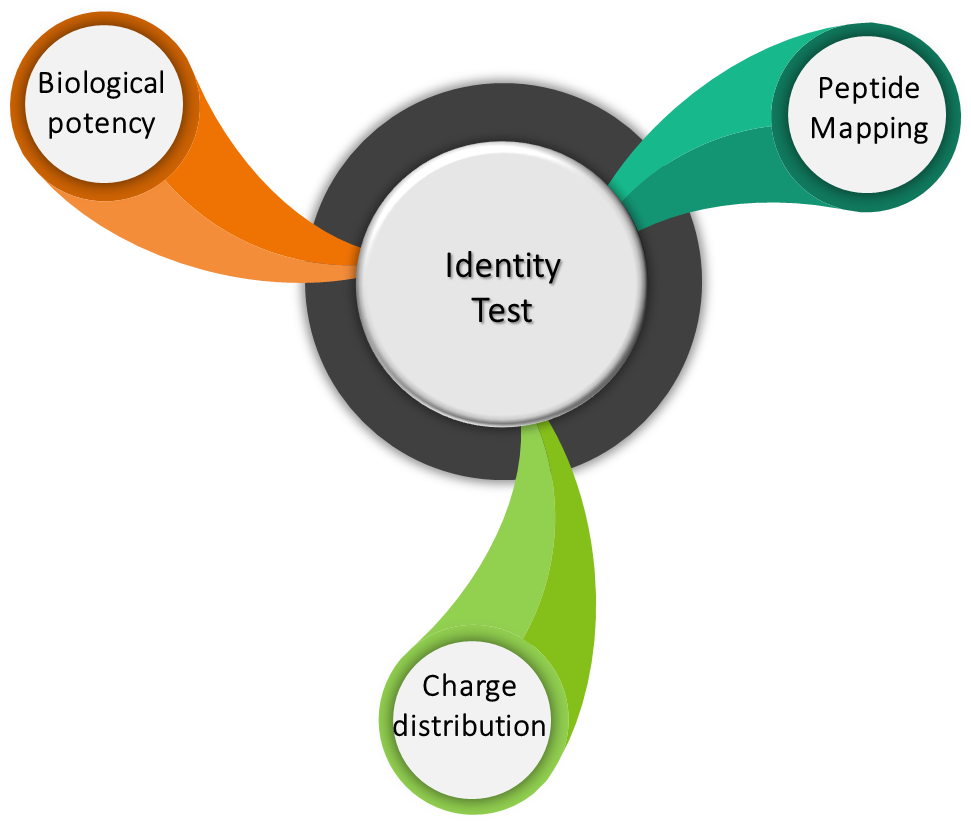
What is Peptide Mapping?
Peptide mapping is a widely used analytical technique to identify and/or to verify a primary structure of biologics. It is one of the most widely used identity tests for testing in-process samples, drug substances, and drug product release.
How is Peptide Mapping performed?
The peptide mapping workflow involves endo-peptidase digestion of the protein followed by separation of peptides by reversed phase liquid chromatography. The procedure generates a 'fingerprint' or set of unique peptides of the protein that will be compared to the reference standard.
What we provide?
Using our expertise in various analytical technologies and knowledge in cGLP, cGMP, and other regulatory guidelines, we provide a wide range of analytical services to support biopharmaceutical product development, including identity testing.
What is Charge Variants Profile?
Molecular variants of biologics, with differences in their charge, are known as charge variants. These charge variants are generally acidic or basic in nature and are compared with the main species. In the identity test, the charge variants profile of the test sample is compared to the reference standard profile.
How are Charge Variants measured?
Charge variants can be separated and measured by orthogonal techniques such as ion exchange chromatography (IEX) and imaged capillary Iso-Electrophoretic focusing (icIEF). In IEX chromatography, molecules are separated based on their surface charge, while in icIEF, molecules are separated based on total charge i.e., Isoelectric point (pI) of the molecule.
What we provide?
We provide charge distribution data by both IEX and icIEF methods as per customer requests. The data obtained from these analyses demonstrate that the main peak is consistent with the expected product and hence, can be used as an identity test. Our laboratories are well equipped with broad analytical technologies such as HPLC, UPLC, icIEF analysis, and LC-MS etc. We are also capable of isolating separated peaks i.e. (single charge variant) using semi-preparative IEX columns. Isolated peaks can be further characterized by LC-MS as per regulatory requirements.
What is Potency?
Potency is a quantitative measure of biological activity of a biomolecule. Potency measures the ability of biologics to trigger specific responses in a disease-relevant system. Potency is a critical quality attribute in manufacturing process of biologics and is often determined by mechanism of action based biologically relevant assay.
How is Potency measured?
Biological activity is the specific ability of a biologic to achieve a desired biological effect. The results of biological assays should be expressed in units of activity calibrated against a reference standard, when applicable, for the assay utilised. Relative potency is measured by comparing the concentration-response curves of a test batch with that of a reference standard.
What we provide?
We provide the services to measure the biological potency of biologics including plate based binding assays, cell based binding assays and cell-based bioassays and/or as per customer request. Since binding is very specific to the molecule, this method can be used as an identity test method.
Test